Glucovance (Glyburide + Metformin)











Dosages
Glucovance 2.5mg/400mg
| Quantity | Price per pill | Total price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | $1.60 | $48.00 | |
| 60 | $1.35 | $81.00 | |
| 90 | $1.23 | $111.00 | |
| 120 | $1.16 | $139.00 | |
| 180 | $1.08 | $194.00 | |
| 270 | $1.00 | $270.00 | |
| 360 | $0.80 | $288.00 |
Glucovance 5mg/500mg
| Quantity | Price per pill | Total price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | $1.70 | $51.00 | |
| 60 | $1.50 | $90.00 | |
| 90 | $1.40 | $126.00 | |
| 120 | $1.33 | $160.00 | |
| 180 | $1.27 | $228.00 | |
| 270 | $1.20 | $324.00 | |
| 360 | $0.95 | $342.00 |
Payment & Shipping
Your order is securely packed and usually ships within 24 hours. Here's what a typical package looks like.
It is about the size of a regular letter (9.4x4.3x0.3 inches) and shows no details about what is inside.



| Shipping Method | Estimated delivery |
|---|---|
| Express Free for orders over $300.00 | Estimated delivery to the U.S.: 4-7 days |
| Standard Free for orders over $200.00 | Estimated delivery to the U.S.: 14-21 days |









Discount Coupons
- Independence Day - July 4, 2026 10% JULY410
- Labor Day - September 7, 2026 7% LABOR07
- Thanksgiving - November 26, 2026 9% THANKS09
Brand Names
| Manufacturer | Brand Names |
|---|---|
| Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. | Glucored |
FAQ
Description
What is Glucovance?
Glucovance (Glyburide + Metformin) is a generic prescription drug that comes in pill form for oral use. The drug is used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. This pharmaceutical product is a combination of two molecules in one form: glyburide and metformin molecules. Glyburide belongs to the class of sulfonylureas.
Metformin belongs to the class of biguanides. Both substances are designed to control blood sugar levels in patients with type 2 diabetes. The combination of two molecules in a single form makes it possible to enhance the therapeutic effect of each of them.
Who Is It Suitable For?
Glucovance is a pharmaceutical product for the treatment of symptoms of type 2 diabetes mellitus. It can be used as monotherapy or in combination with other drugs. At the moment, nothing is known about the safety of the drug for children. Its usage by pregnant and nursing women should be motivated by irreplaceability and high necessity for the patient.
How Does It Work?
Glucovance should be taken in conjunction with the exercise program and diet prescribed by a certified doctor. Glyburide lowers blood glucose levels by stimulating the release of natural insulin and inhibiting liver function to produce sugar. Metformin also affects the liver in terms of reducing the level of glucose produced. The combination of glyburide and metformin is designed to help the patient restore the body's normal response to natural insulin produced by the body.
Glucovance Precautions to Be Aware of
Despite the relative safety of Glucovance, the manufacturer strongly recommends you to read a number of warnings and contraindications.
Warnings
Glucovance has a number of warnings regarding the use, the main one of which is the FDA Warning regarding the possible provocation of such a condition as lactic acidosis by the drug. This pathological condition is associated with a decrease in the level of oxygen in the blood, which can provoke the accumulation of lactic acid in the bloodstream. This condition is quite serious from the point of view of danger to the patient and can lead to fatal consequences. If a patient has diabetes with kidney damage or heart failure, the risk of lactic acidosis is quite high.
Also, the manufacturer of the drug warns the patient about the risks associated with:
- surgical operation;
- undergoing an MRI or CT scan;
- any other procedure.
The doctor must decide to temporarily stop taking the drug for patients in all cases where contrast dyes are injected into the patient's body. The fact is that glyburide or metformin interacting with contrast iodine-containing substances can provoke renal failure or lactic acidosis.
Another warning concerns sensitivity to the sun, which can be triggered by taking Glucovance. The probability of sunburn when taking glyburide or metformin increases. This applies both to being in the open sun and staying in tanning salons, which should be abandoned while taking the drug.
The manufacturer also warns about the risk of hypoglycemia, since both active components of the Glucovance drug contribute to an intensive decrease in blood glucose levels. The symptoms of hypoglycemia are as follows:
- wobbly gait;
- nervousness;
- sweating, chills;
- irritability;
- confusion of consciousness;
- tachycardia;
- dizziness;
- severe hunger;
- nausea;
- drowsiness;
- visual impairment;
- tingling or numbness of the lips or tongue;
- headaches;
- increased fatigue.
If these symptoms are detected, you should consult a doctor and act in accordance with the recommendations regarding hypoglycemia.
Contraindications
The pharmaceutical product is contraindicated to patients with the following pathologies:
- kidney disease or renal dysfunction;
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- acute or chronic metabolic acidosis.
The simultaneous use of bosentan together with Glucovance is also unacceptable. In addition, as mentioned above, patients undergoing radiological examination with the introduction of iodine-containing contrast materials should temporarily refuse to take the drug in accordance with the recommendations of the attending physician.
Cautions
Glucovance may cause hypoglycemia or its symptoms. Therefore, it is important for the patient to observe the regimen and dosage of the drug. The following categories of patients are considered to be the most susceptible to hypoglycemic effects:
- Physically and mentally exhausted patients.
- Elderly people.
- Patients with pituitary or adrenal insufficiency.
- Alcohol abusers.
Glyburide as an active component of the drug can cause hemolytic anemia. Therapy in patients with G6PD deficiency should be carried out under the full supervision of a doctor, since post-marketing reports inform about the detection of hemolytic anemia in such patients.
It is also worth understanding that metformin hydrochloride is largely excreted from the body with the help of the kidneys, so the accumulation of the substance increases the risk of renal disorders. Therefore, when elderly patients take the drug, it is necessary to continuously monitor kidney function. As a rule, the maximum permissible dose of the drug is not prescribed to such patients. The doctor should make sure that the patient's kidney function is normal before prescribing the drug.
It is necessary to combine the drug as carefully as possible with concomitant drugs that may affect renal function, hemodynamics or metformin utilization. Patients with heart failure or with post-infarction conditions should note take the drug in order to avoid prerenal azotemia.
Pregnancy And Lactation
It has been proven that abnormal blood glucose levels can lead to congenital fetal abnormalities. Since Glucovance is tested exclusively on pregnant animals, there is no direct evidence that it will not harm the baby. Therefore, it is not recommended to take the drug during pregnancy, except in cases where it is really necessary.
There was a study on the effect of glyburide on the reproductive function of rats and rabbits. At the same time, there was no evidence of fertility disorders or harm to the fetus. The study of metformin hydrochloride for the teratogenic effect on rabbits and rats proved the absence of such.
There have also been studies related to the use of drugs of the pharmacological group of sulfonylureas during pregnancy. Prolonged severe hypoglycemia was detected in newborns from mothers who took sulfonylureas during pregnancy. Therefore, you should stop taking the drug within at least 2 weeks before the expected delivery.
As for studies related to lactation, it is currently unknown whether glyburide is excreted in breast milk. At the same time, it is known that some sulfonylureas enter the mother's milk. Therefore, a choice should be made during lactation - either stop breastfeeding or temporarily refuse to take the drug in order to avoid hypoglycemia in a breastfed child.
When making a decision, the importance of therapy for the mother is taken into account. An alternative to taking Glucovance for pregnant women may be therapy using insulin to control blood sugar levels.
Glucovance Dosage
An individual dose of Glucovance is selected by the doctor for each patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus. When prescribing this drug, the doctor should be guided by the tolerability and effectiveness of the drug for a particular patient. The dosage should not exceed the maximum recommended daily dose.
Table 1
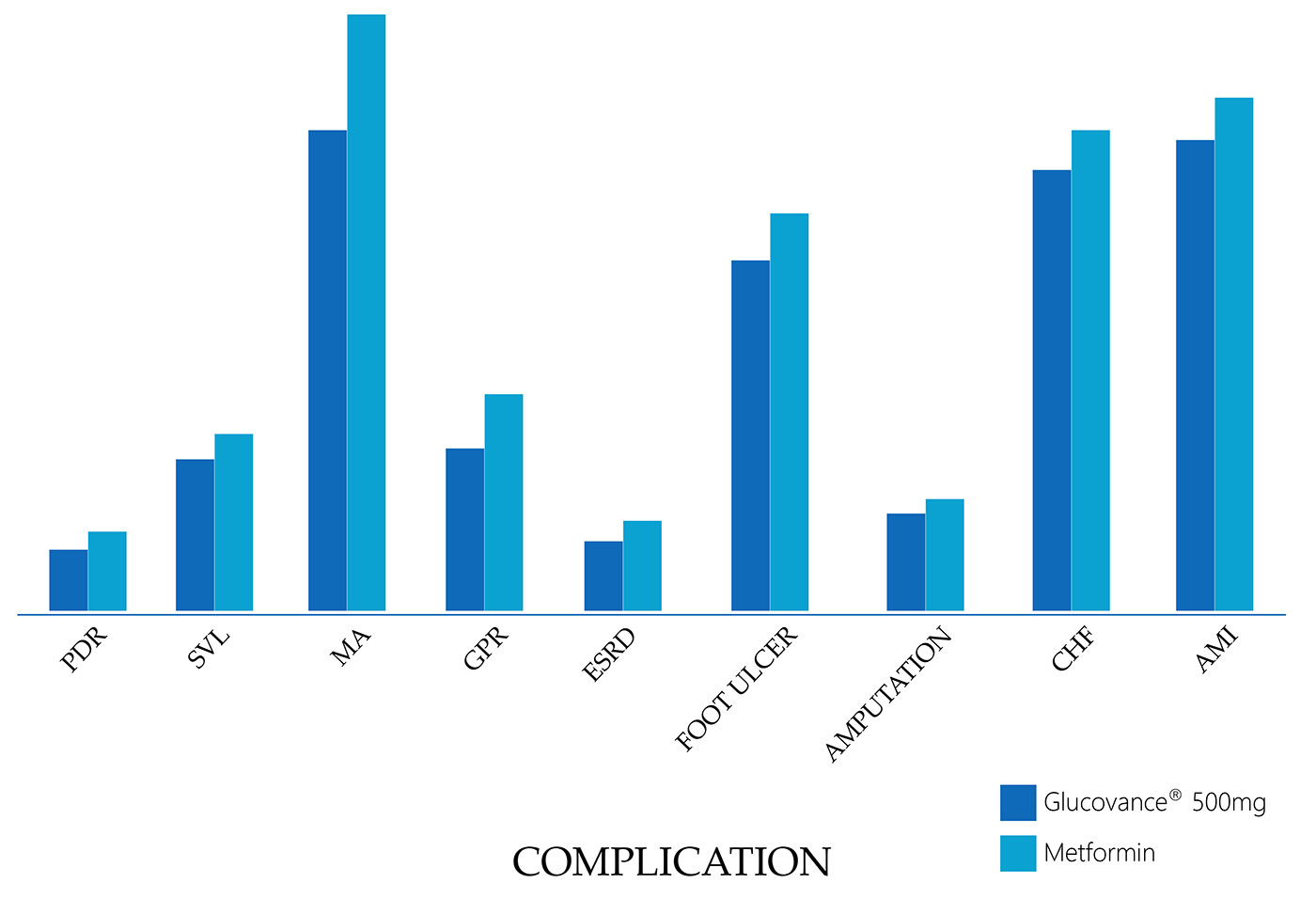
Treatment Emergent Symptoms of Hypoglicemia or Gastrointestinal Adverse Events in Placebo- and Active-Controlled Trial of GLUCOVANCE as Initial Therapy
| Variable | Placebo N=161 | Glibenclamide Tablets N=160 | Metformin Tablets N=159 | GLUCOVANCE 250 mg/1.25 mg Tablets N=158 | GLUCOVANCE 500 mg/2.5 mg Tablets N=162 |
| Mean Final Dose | 0 mg | 5.3 mg | 1317 mg | 557/2.78 mg | 824/4.1 mg |
| Number (%) of patients with symptoms of hypoglikemia | 5 (3.1) | 34 (21.3) | 5 (3.1) | 18 (11.4) | 61 (37.7) |
| Number (%) of patients with gastrointestinal adverse events | 39 (24.2) | 38 (23.8) | 69 (43.3) | 50 (31.6) | 62 (38.3) |
How and When to Take It
Glucovance is taken with meals. Therapy begins with a small dose followed by a gradual increase to an effective dose. The dosage should be increased gradually to prevent hypoglycemia and reduce the likelihood of side effects from the gastrointestinal tract.
This treatment regimen allows you to identify the minimum effective dose for monitoring the patient's condition. Recommended starting dose: 1.25 mg / 250 mg 1-2 times a day. After that, the dosage should gradually increase in increments of 1.25 mg / 250 mg every two weeks.
At the beginning of therapy, the patient's blood sugar level should be monitored. This is necessary to determine the minimum effective dose. Patients with a tendency to hypoglycemia should start treatment with a minimum dose of 1 time per day.
NB! Patients taking colesevelam together with Glucovance should take the drugs with a time gap of at least 4 hours.
Maximum Dose
The maximum recommended daily dose is:
- 20 mg of glyburide;
- 2000 mg of metformin.
Exceeding the maximum allowed daily dose can cause serious side effects.
What If I Miss A Dose
If you have missed taking the drug for several hours, you can safely take the right dosage. If you have missed taking the drug for the time close to the interval between taking the drug, then just take the drug the next time according to the schedule. Do not take a double dose of the drug.
Interaction With Other Products
When taking the drug, the patient should be informed about the interaction of the substances that make up Glucovance with other drugs and substances. The most frequent and sensitive interactions are listed below.
Alcohol/Food Interactions
The effect of metformin on lactate metabolism is evidently enhanced, therefore, a patient taking Glucovance should limit himself/herself from active alcohol consumption. Also, the effect of the drug on the gluconeogenic ability of the liver increases the risk of hypoglycemic conditions. Ideally, a patient suffering from type 2 diabetes mellitus and taking the drug Glucovance should give up alcohol or minimize its consumption.
Other Medications
A number of pharmaceutical drugs can lead to loss of control over blood sugar levels. The list of such drugs includes:
- diuretics;
- corticosteroids;
- phenothiazines;
- thyroid preparations;
- estrogens;
- oral contraceptives;
- phenytoin;
- nicotinic acid;
- sympathomimetics;
- drugs that block calcium channels;
- isoniazid.
When administering these drugs together with Glucovance, the patient needs to ensure the most careful monitoring of blood sugar levels. At the same time, metformin is less likely to interact with other drugs due to insignificant binding to plasma proteins, which cannot be noted about sulfonylureas.
Also, the hypoglycemic effect of a sulfonylurea can be enhanced by a number of substances, including:
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- salicylates;
- sulfonamides;
- chloramphenicol;
- probenecid;
- coumarins;
- monoamine oxidase inhibitors;
- beta-blockers.
The risk of increased liver enzymes is fixed in patients who simultaneously take glyburide and bosentan. There were mentions of a possible interaction between glyburide and a number of antibiotics, including ciprofloxacin and fluoroquinolone, which enhance the hypoglycemic effect of glyburide.
At the moment by 2022, the mechanism of this interaction has not been studied. Interactions with oral miconazole, colesevelam, furosemide, nifedipine, and a number of cationic drugs were also recorded. Studies conducted on volunteers showed no interaction with propranolol and ibuprofen.
What Are the Possible Side Effects of Glucovance?
Common Side Effects
The common side effects identified in the study of the effect of the Glucovance drug include:
- upper respiratory tract infection;
- diarrhea;
- headache;
- nausea/vomiting;
- abdominal pain;
- dizziness.
No episodes of intense uncontrolled hypoglycemia were detected in the controlled clinical trials of Glucovance. Disulfiram-like reactions have also been very rarely reported in patients taking glyburide in pill form.
Table 2
GLUCOVANCE`s Most Common Clinical Adverse Events (>5%) When Compared to Placebo, by Primary Term, in Double-Blind Clinical Studies
| Adverse Event | Number (%) of Patients | |||
| Placebo N=161 | Glibenclamide N=324 | Metformin N=312 | Glucovance N=642 | |
| Upper respiratory infection | 22 (13.7) | 57 (17.6) | 51 (16.3) | 111(17.3) |
| Diarrhea | 9 (5.6) | 20 (6.2) | 64 (20.5) | 109 (17.0) |
| Headache | 17 (10.6) | 37 (11.4) | 29 (9.3) | 57 (8.9) |
| Nausea/Vomiting | 10 (6.2) | 17 (5.2) | 38 (12.2) | 49 (9.6) |
| Abdominal Pain | 6 (3.7) | 10 (3.1) | 25 (8.0) | 44 (6.9) |
| Dizziness | 7 (4.3) | 18 (5.6) | 12 (3.8) | 35 (5.5) |
Serious Side Effects
There were no serious side effects with the proper use of Glucovance. The drug is considered safe, but, nevertheless, requires strict adherence to the dosage and compatibility with other pharmaceutical products. Severe hypoglycemic reactions, including those accompanied by coma, which constitute a medical emergency, can occur only as a result of an overdose of glyburide.
Glucovance (Glibenclamide + Metformin) Drug Overdose
Overdose with glyburide pills can provoke hypoglycemia. When a symptom occurs, the doctor should adjust the dosage, diet, and physical activity of the patient. If an overdose has led to a hypoglycemic coma, it is necessary to urgently inject the patient with a 50% glucose solution. Such patients should be under the close supervision of a doctor for several days.
Hypoglycemia is observed less frequently in the case of metformin hydrochloride overdose. According to studies, there are no more than 10% of such cases, and the researchers failed to prove a direct link with an overdose of the drug and a hypoglycemic condition. As for lactic acidosis, it manifests itself in 32% of cases of metformin overdose. In this case, hemodialysis can be used to remove the accumulated drug from the body.
Drugs Similar to Glucovance (Glyburide + Metformin)
Several drugs similar to Glucovance, a combination of glyburide and metformin, offer dual-action approaches to managing diabetes.
One notable alternative is Janumet, which combines sitagliptin, a DPP-4 inhibitor, with metformin, targeting both insulin resistance and glucose production.
Another option is Xigduo XR, pairing dapagliflozin, an SGLT-2 inhibitor, with metformin, promoting glucose excretion via the kidneys while reducing hepatic glucose output.
Additionally, Amaryl that includes glimepiride, a sulfonylurea like glyburide, stimulating insulin secretion while improving insulin sensitivity. For patients seeking alternatives due to intolerances or contraindications, these medications offer diverse mechanisms of action, catering to individual needs for effective glycemic control.