Hypoglycemia, or hypo, refer to a low blood glucose value below 3,9 mmol/L or 70 mg/dl (1, 2). This is the international consensus for a definition of hypoglycemia from American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical Care, in three levels.
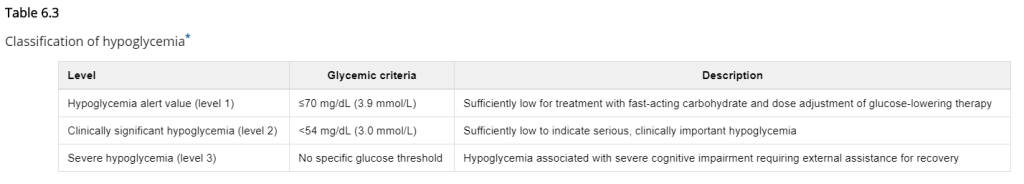
Severe hypoglycaemia and a very low glucose can lead to coma and death (global mortality due to hypoglycemia 3, detailed paper about complications 4). Hypoglycemia can happen due to a number of reasons; too much insulin, not eating enough carbs, intensive physical activity, heat such as sauna or a hot bath, intramuscular insulin injection, alcohol, among others. It´s important to inform friends and family about symptoms of hypoglycemia, some are (please note that not all must be present):
- Unconsciousness/coma
- Irregular heartbeat
- Shaky or jittery
- Pale
- Hungry
- Anxiety
- Sweaty
- Irritable
- Confused or disoriented
- Issues concentrating
- Memory impairment
- Slurred speech
- Being stroppy
- Muscle cramps
IMPORTANT: Inform your friends, family and colleagues about the above, and save the picture below for tips how to handle an emergency situation. Never ever under any circumstances give insulin.

References:
- http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/41/Supplement_1/S55
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/preventing-problems/low-blood-glucose-hypoglycemia
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00125-018-4626-y
- https://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/36/5/1384?ijkey=9f30ad723a9cdf1df3f1e61cc160c60f3a6426c0&keytype2=tf_ipsecsha&fbclid=IwAR2pOxVYmwV61qgrf7TiLJlDEYJ7xkk6O4n1YBYCruBSnLUOypdJQXLJ0gQ


























