At first sight, the question seems strange. Isn’t hyperglycemia the main concern in diabetes type 2?
Surprisingly, people with diabetes type 2 don’t only suffer from high blood sugar. The majority of patients acquire the condition of hypoglycemia due to the prolonged exposure to medicines lowering blood sugar. The condition when blood sugar falls too low is called hypoglycemia.
Still, the issue of hypoglycemia and type 2 diabetes remains open since not in all cases the reasons are the same.
Type 2 Diabetes And Hypoglycemia
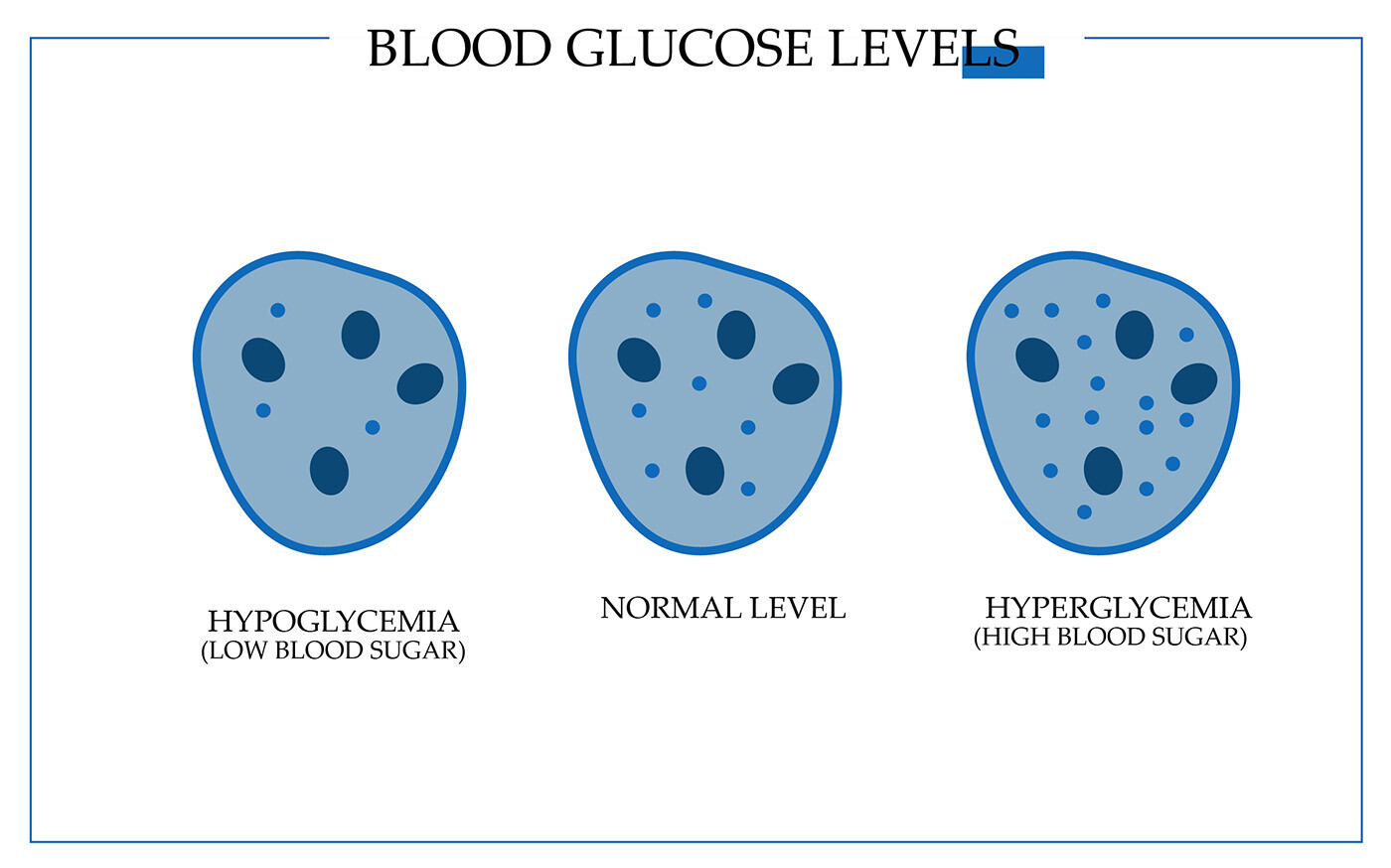
In reality, hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes occurs quite often. The hazard is that many people don’t know about it because they neglect to test their blood sugar and don’t take it under control. A person whose hypoglycemia lasts already long can simply get used to the diabetes type 2 hypoglycemia symptoms. This can lead to unawareness of hypoglycemia. So, the only way to find out about it is to measure blood sugar levels on a regular basis.
Why Type 2 Diabetics Need to Be More Aware of Hypoglycemia?
The risks of getting hypoglycemia concern every diabetic. The potential risk is too high, and patients need to know about it. As a rule, people over 65 who take insulin to treat diabetes happen to be at a greater risk of having hypoglycemia and more frequently develop complications in the form of seizures, loss of consciousness, or diabetic coma.
The odds of having this condition are revealed to be higher in patients who are on insulin or combine insulin with oral hypoglycemia agents. Low blood sugar can be hard to spot and that is why type 2 diabetics need to keep an eye on their blood sugar indicators.
Frequency Of Hypoglycemia In Type 2 Diabetes
The issue is more common than we know. But first of all, let us give the answer to the popular inquiry ‘What is the difference between hypoglycemia and diabetes type 2?’ In fact, hypoglycemia is the condition that might go with type 2 diabetes due to treating diabetes.
So, how often does hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes occur? Both moderate and severe forms of hypoglycemia were found in almost half of insulin-treated patients – over 45% of people were recorded to have sugar-drop incidents, 7.3% out of which are likely to require emergency medical help. This was proven by the study lasting 12 months to identify the events of low blood sugar in both diabetes type 1 and 2 patients.
Such frequency of hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes patients makes it worth measuring blood sugar more often and be attentive to any signals of the condition.
When Is Blood Sugar Considered to Be Too Low

Generally, anything below the level of 70 mg per deciliter, or 3.9 millimoles per liter, is considered dangerously low. However, the numbers might vary from patient to patient so a consultation with the doctor is needed.
What Causes Type 2 Diabetes Hypoglycemia
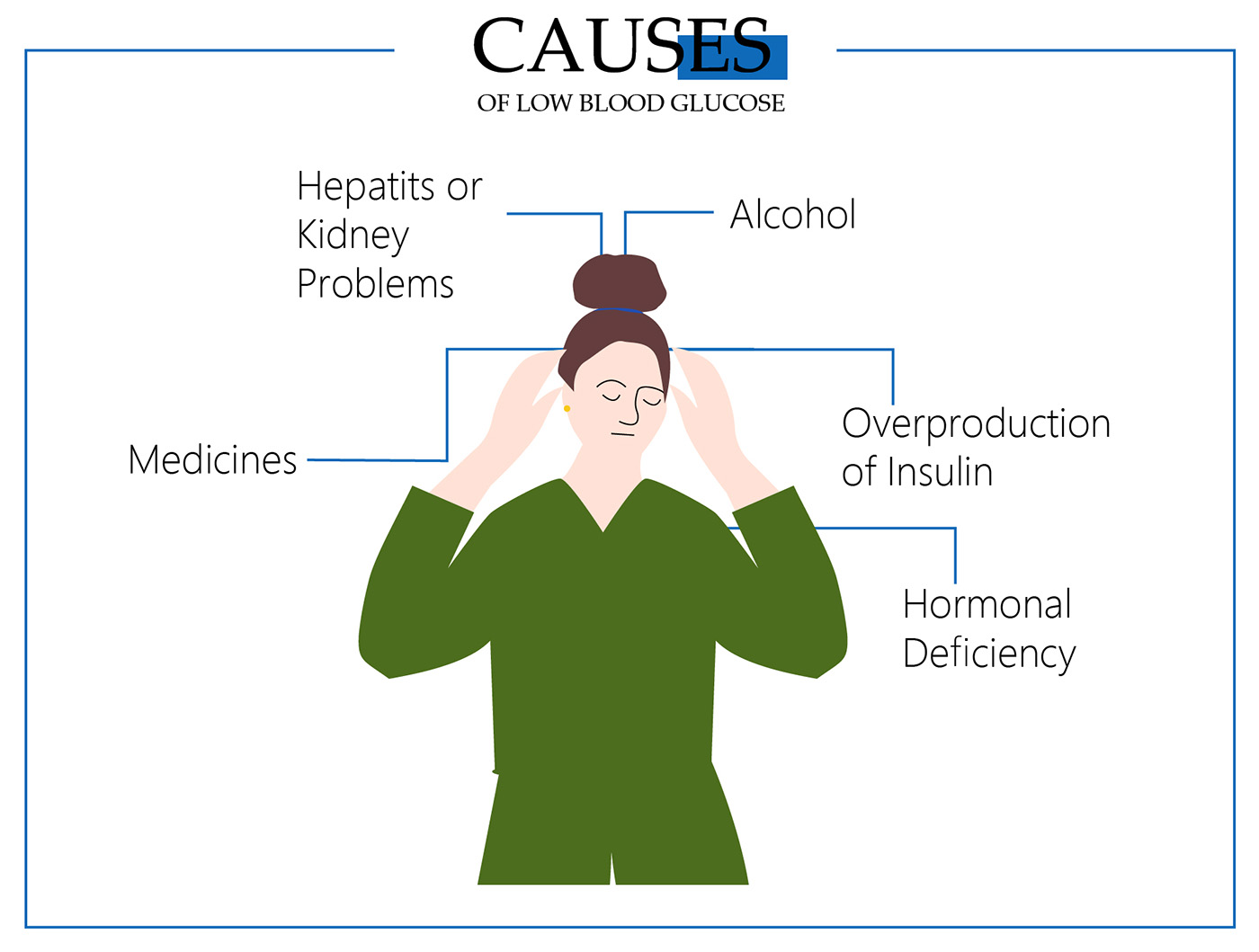
In patients treating diabetes type 2, low blood sugar is mostly caused by regulating blood sugar with medications.
As you already know, glucose can enter the cells only with the help of insulin which is the hormone produced by the pancreas. Whenever you have a meal, your glucose level rises and the stored glycogen is released into the bloodstream. Still, the body of a diabetic is unable to regulate this glucose level and a doctor prescribes medicines.
The only problem is that medicines like insulin have to be injected in the exact amount that is defined by the doctor. In case the dose is higher, it causes a sudden drop in blood sugar.
Other reasons for hypoglycemia except for type 2 diabetes hypoglycemia might be taking up a sudden physical activity, consuming not enough carbs, delaying meals or eating very rarely, suffering from insulin overproduction and cortisol or thyroid hormone deficiencies, and indulging in alcohol. Some of the most common reasons are described below.
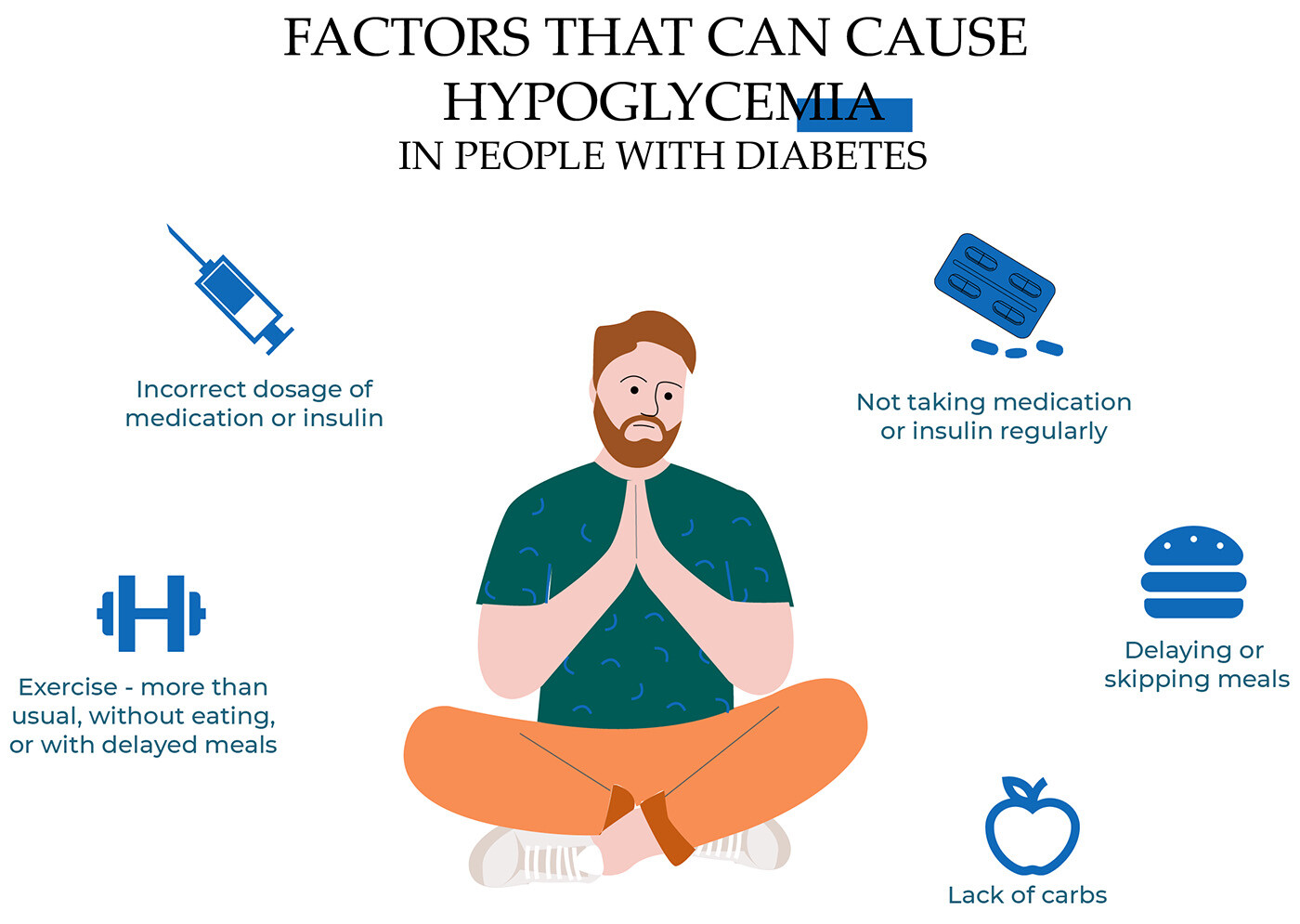
Engaging In A Sudden Physical Activity
If a patient increases their physical activity over the typical amount without the doctor changing the dose of medicine, the blood sugar level tends to fall down. The effect can stay up to 24 hours after exercise.
The way out is to discuss with the doctor every possible growth of the time or intensity of your workouts.
Not Eating Enough Carbohydrates
Why do we speak of carbohydrates here? Mainly because it is carbs that get broken down to glucose which raises the blood sugar level.
Eating the right amount of carbohydrates is the key to balancing the activity of medication to avert hypoglycemia. If you don’t know how to harmonize carbs, fats, and proteins on your plate for them to match your dose of medicine, please, consult a healthcare expert.
Skipping or Postponing Meals
The longer you don’t eat anything the lower your blood sugar drops. Lasting ‘windows’ between meals are not recommended for anyone suffering from hypoglycemia due to type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Such drops can happen during nighttime when you naturally aren’t eating for a long time. See a doctor to regulate this.
Drinking Too Much Alcohol
Can alcohol cause diabetes 2 hypoglycemia? Only in certain conditions. Consuming alcoholic beverages, especially when a patient hasn’t eaten for a long time, is very undesirable. This doesn’t only lead to type 2 diabetes hypoglycemia but also makes the symptoms of type 2 diabetes and hypoglycemia less noticeable.
Some Type 2 Diabetes Medications
Drug therapy with insulin and the types of medicines known as sulfonylureas and meglitinides increases the chances of developing type 2 diabetes with hypoglycemia.
Common medications that are able to cause low blood sugar include:
|
Name of substance |
Other names / names of medications |
|
insulin |
|
|
glimepiride |
Amaryl |
|
glipizide |
Glucotrol, Glucotrol XL |
|
nateglinide |
Starlix |
|
glyburide |
Glynase, Micronase, DiaBeta |
|
repaglinide |
Prandin |
Pills containing any of these substances may drive hypoglycemia too.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hypoglycemia?
According to American Diabetes Association, the most widely spread diabetes type 2 hypoglycemia symptoms include:
|
Symptoms during daytime |
Symptoms during the night |
|
|
In cases with severe hypoglycemia, patients have more serious hypoglycemic symptoms: they lose the ability to eat or drink, might have convulsions, or become unconscious. Such cases need emergency medical treatment.
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Hypoglycemia Prevented
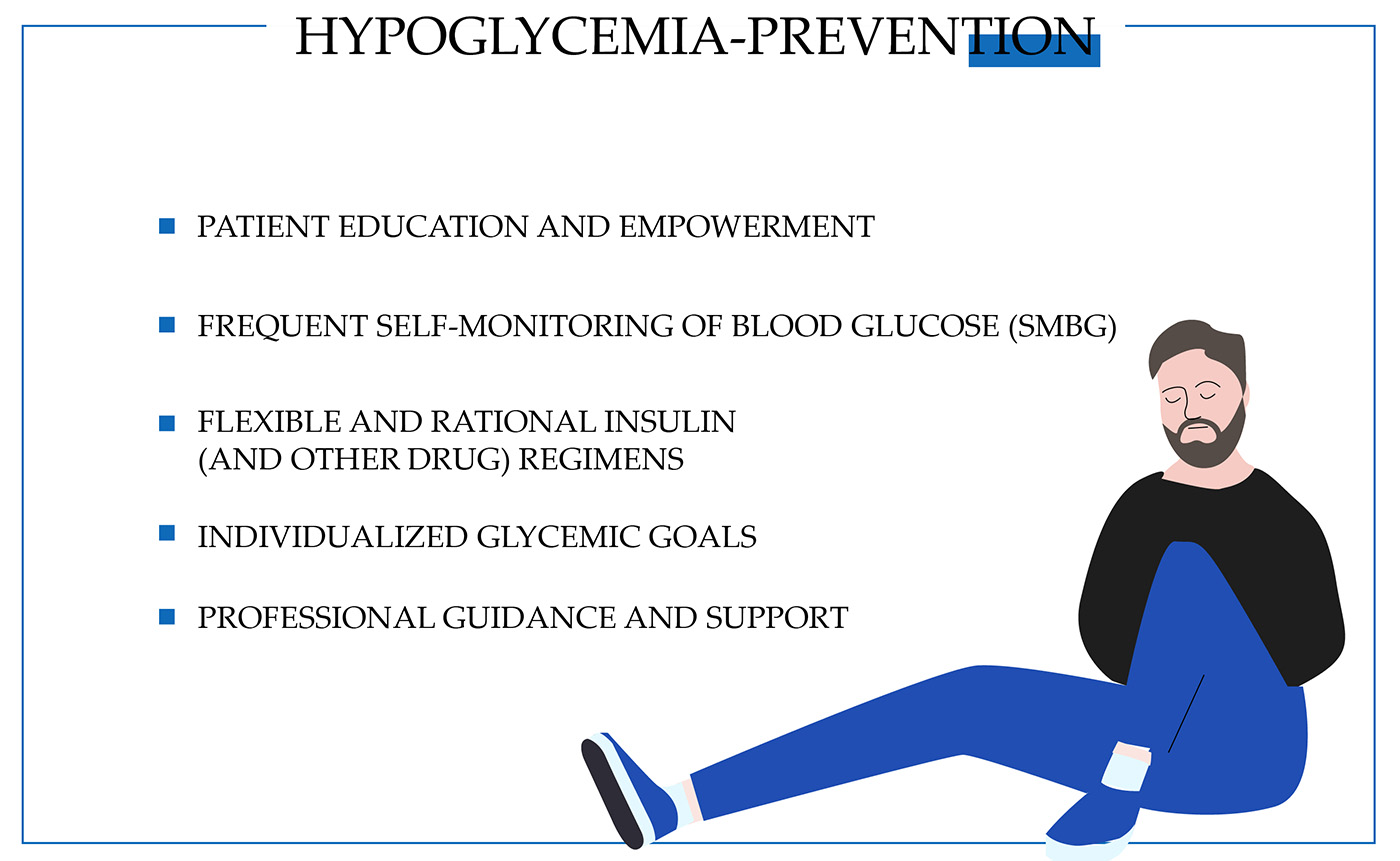
There are a few things you can do to ward off type 2 diabetes hypoglycemia in your life or the life of a close person.
Diet
Maintaining a healthy and balanced diet is something that can effectively prevent the symptoms and block type 2 diabetes and hypoglycemia.
- Being careful with alcohol, especially on an empty stomach, or abstaining from it at all.
- Not skipping meals (perfectly, having and sticking to an eating plan). This can cover having both meals and snacks during the day.
- Eating healthy carbohydrates and having a carb snack before physical activities to lower the odds of hypoglycemia.
Physical Activity
One thing that everybody with type 2 diabetes must do is to discuss the amount of exercise in daily life and ways to balance medication and physical activity. Exercising is a powerful way to reduce blood glucose and hence, it should be used wisely.
Medication
- Measuring blood glucose levels regularly.
- Always having the necessary medications with you (such as glucagon injections) to overcome symptoms when they start to arrive. Carrying glucose tablets or candies is also helpful.
Talk to your doctor about prescriptions and doses before you make workouts more intense.
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Hypoglycemia Treated?
Treatment of hypoglycemia is generally divided into immediate and long-term. In case you need to raise your blood sugar level urgently, taking medications or drinks with high sugar percentages are the popular steps.
However, treating this condition in perspective requires identifying the real cause of hypoglycemia. Read the Section ‘What Causes Type 2 Diabetes Hypoglycemia’ and consult a specialist to do this.
But the first thing to do if a person has the symptoms of hypoglycemia and type 2 diabetes is to measure their blood glucose. If the signals are mild, the situation can be corrected by seeing a specialist and required bringing changes to the eating plan, exercising routine, diet, or medicine intake.
More severe cases of hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes are often treated by prescribing hormonal therapy (in the form of glucagon injections). There are many forms available over the counter including regular kits and pre-mixed substances. Your doctor will advise the best version for you to quickly respond to any symptom bothering you.
What you should NOT do when having or seeing someone have a fit or experiencing one of the hypoglycemia symptoms is inject insulin since this can make blood glucose go down even more.
Offering solid food or liquids can also be dangerous since a patient can feel too weak to eat anything or is likely to choke. The exception is a candy or a sugary drink which helps to overcome symptoms of hypoglycemia.
The Takeaway
Hypoglycemia is a condition that can accompany type 2 diabetes and is revealed when blood sugar drops below the norm. It can be treated more easily at the first mild stages and requires regular checks of blood glucose levels. Severe cases, however, demand more radical treatment such as glucagon therapy. The key to successful treatment is noticing the symptoms early, consulting the doctor, and together deciding on the measures to prevent the development of the condition.
FAQ
Can Type 2 Diabetes Have Hypoglycemia?
Hypoglycemia often occurs in type 2 diabetics which means their blood sugar drops below 70 mh\dl.
How Common Is Hypoglycemia In Type 2 Diabetes?
The group of patients most commonly developing hypoglycemia as an effect of treating type 2 diabetes is the ones using insulin, sulfonylureas, and meglitinides. The frequency makes 45% with the calculated frequency of episodes of nearly 17 per year for one patient.
Can Alcohol Cause Diabetes 2 Hypoglycemia?
Consuming alcohol can be a part of a healthy diet only when it includes moderate amounts and does not occur when a person is hungry. In case alcohol is taken at the wrong time (after 2-3 hours of eating nothing), this can cause hypoglycemia, especially with type 2 diabetes in the background.


























