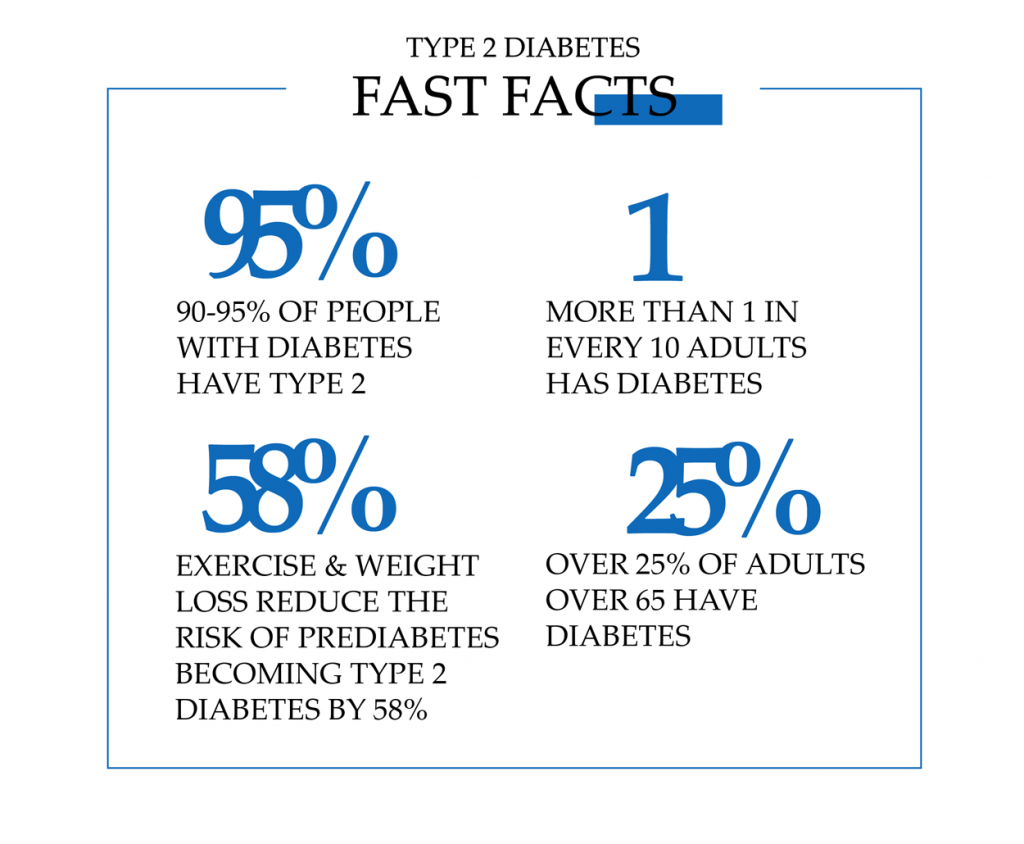
According to statistics, at least one person in every 10 people suffers from diabetes. Most patients who are diagnosed with diabetes, have type 2 diabetes mellitus. The older the person, the higher the risk of being diagnosed with this serious disease. Find out when you should consult the doctor and how to prevent risks of diabetes 2.
What Is Type 2 Diabetes?
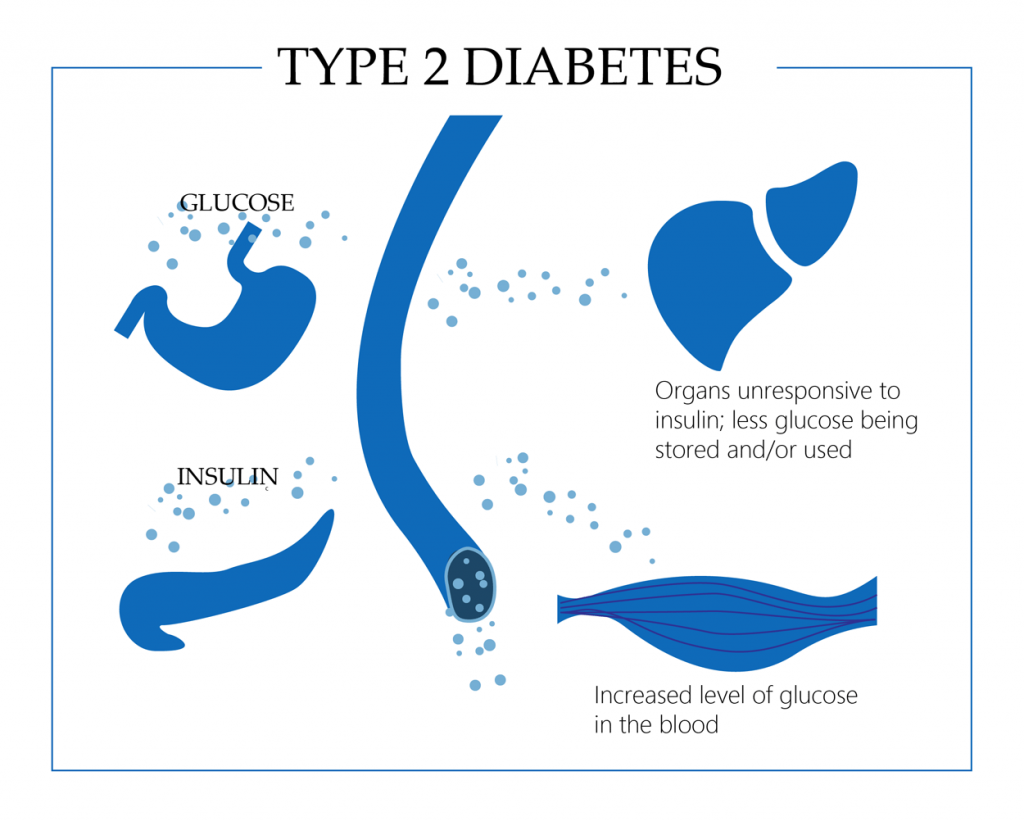
So, what is type 2 diabetes? It is a disease that is characterized by metabolic disorders that lead to hyperglycemia. The high level of glucose in the blood occurs when the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin become unable to produce enough of it, or when the insulin produced is not accepted by the body – a condition also known as insulin resistance. Unfortunately, this disease is lifelong. But if you are armed with the right information, develop an adequate attitude, and adhere to the right lifestyle, you can live a full and healthy life.
What is worse type 1 or type 2 diabetes? Type 1 and type 2 diabetes differ in several ways. Unlike type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes usually occurs in people over the age of 40-45. However, an unhealthy diet and lifestyle can contribute to the development of diabetes at any age. It used to be called mature diabetes because it was more common among older people, but with increasing obesity and a more sedentary lifestyle of young people, the risk for young adults, adolescents, and children has grown.
Another important factor differentiating type 1 and type 2 diabetes is that type 1 diabetes appears within a few weeks. Type 2 diabetes develops slowly over a longer period of time. In this regard, patients sometimes don’t pay attention to the gradually emerging symptoms.
Signs and Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
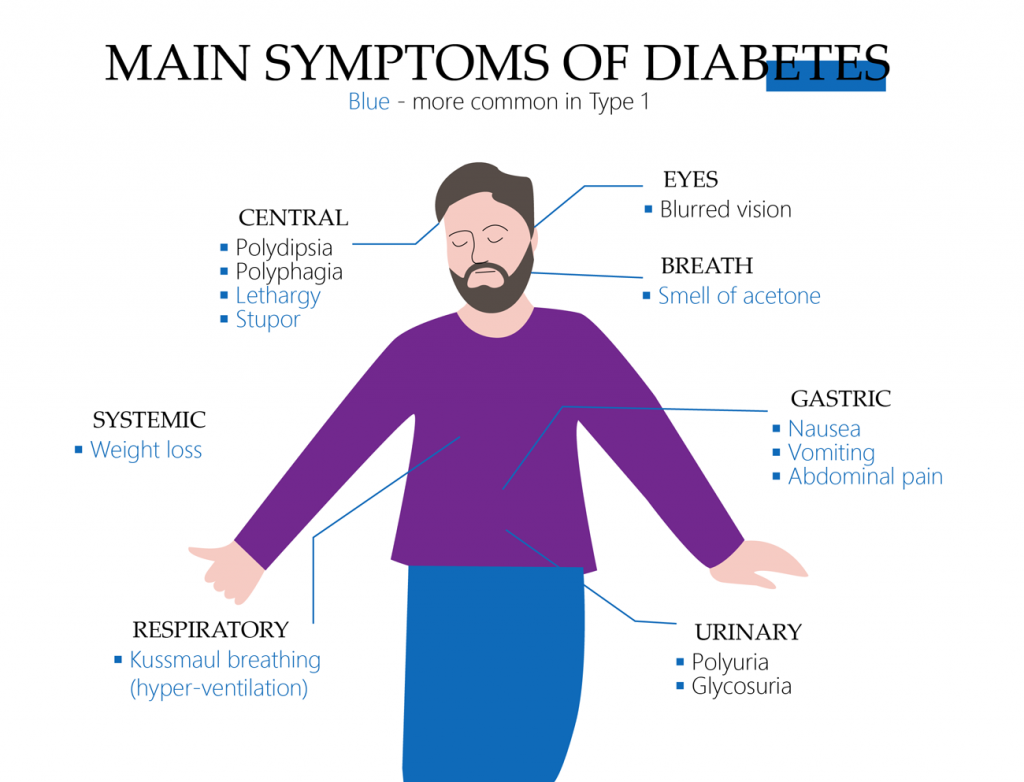
The worst thing about type 2 diabetes is that it is difficult to identify the presence of the disease at the initial stage. Millions of adults around the world have diabetes, but they don’t take any measures because most of them have never taken any tests. There are certain symptoms that may help you to understand that you are at the risk group of diabetes development. However, you should be careful as some of the signs can be symptoms of other diseases as well. What are the symptoms of type 2 diabetes? Those patients who have been diagnosed with 2 type diabetes report the following symptoms.
Being Very Thirsty
Do you drink much and still feel thirsty? It is one of the very first diabetes signs. Don’t hesitate to check your blood sugar level if you are thirsty for a long period, especially if you have more than one sign of diabetes. Remember that thirst and frequent urges for urinating is one more sign of diabetes.
Being Cranky
Do you feel angry, depressed, and suffer from quick mood changes? Of course, being cranky may be not connected with diabetes, but if you have some other symptoms of the disease, don’t forget to inform your doctor about being cranky as well.
Fatigue/Feeling Worn Out
It is normal to feel tired about the long working day. But if you feel exhausted without any reason, it is a bad sign that may mean that you are worn out because you have type 2 diabetes.
Feeling Hungry
One of the must-have diabetes symptoms is the feeling of constant hunger. You want to eat more and more, one portion after another one, and finally, you become obese. It’s a well-known factor that obesity is one of the risk factors that lead to diabetes.
Getting More Infections and Other
People with type 2 diabetes are prone to getting different infections because their immune system is weak. Have you noticed that you get sick easily recently? Don’t avoid this sign of diabetes and tell the doctor about it when describing all the signs.
The pharmacist will have a clear picture of all the symptoms and will identify whether all of them are just separate signs of some other health conditions, or they are interconnected and lead to the development of type 2 diabetes. Testing is needed to identify all the comorbidities of diabetes you have.
What Causes Type 2 Diabetes
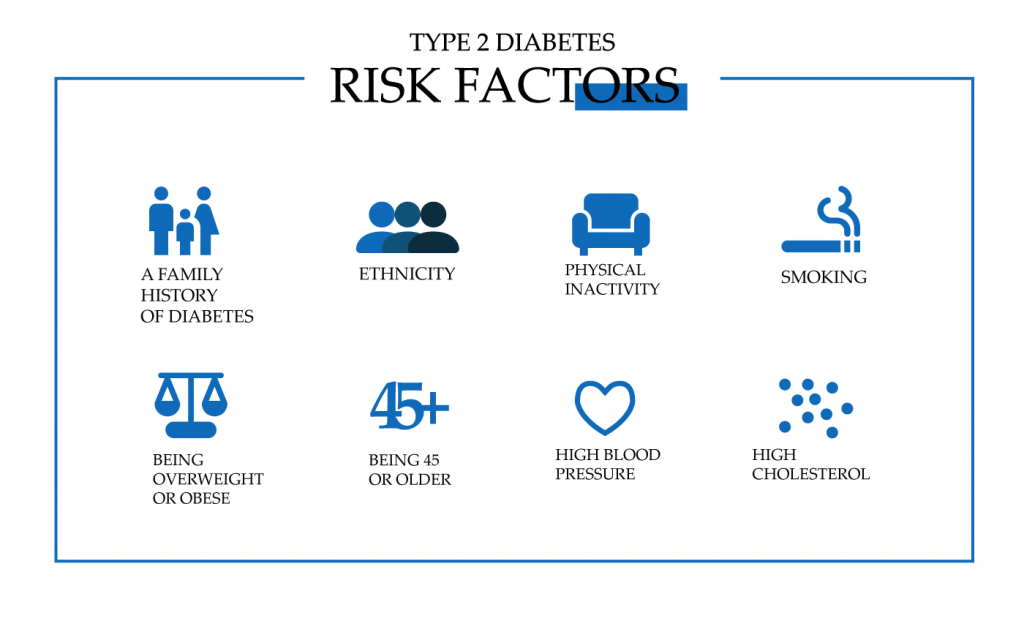
Not everyone knows what causes the 2d type of diabetes. The causes of type 2 diabetes have several origins, among which the main factors are genetics and lifestyle. Despite a number of factors that determine the causes of type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance underlies the disease. This is a condition in which a person with diabetes either does not produce enough insulin or the insulin produced by the body is not processed. Scientists haven’t yet been able to identify which factors act as catalysts for the development of the disease. So far, the causes of type 2 diabetes boil down to a number of risk factors listed below.
Genes
Do you wonder what is the cause for 2 type diabetes? Possible causes of type 2 diabetes include genetics and family history. Despite the importance of this factor, it is not a determining factor in the development of the disease but only increases the risk. If any of your close relatives – mother or father, brother or sister – have this condition, you are at increased risk of developing diabetes. Some have a chronic form of the disease.
Extra Weight
Being overweight can significantly increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. About 90% of people with type 2 diabetes aged 16-54 are overweight or clinically obese. A weight loss program is one of the recommended treatments after diagnosis. The possible extra pounds you have may increase the body’s insulin resistance, which in turn increases the dependence on treatment that requires the introduction of insulin.
Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome isn’t just one special condition. It’s a combination of conditions that may lead to type 2 diabetes. Among such conditions are high blood pressure, extra weight, health conditions that have a negative effect on the functioning of blood vessels. There are certain signs that may help you find out that you have a metabolic syndrome. Usually, the very first sign is the increase of fat around the waist. In case you have it in combination with high blood pressure, don’t waste time and consult your healthcare specialist.
Too Much Glucose from Your Liver
Another possible cause of type 2 diabetes is the condition caused by the excessive amount of glucose that goes from your liver. It happens when the level of blood sugar is low. In this case, the liver starts sending glucose. How does it work? When you consume food, the level of blood sugar increases. Your liver stores glucose each time you eat something. However, it doesn’t mean that your liver will do the same. Sometimes, livers manage to produce sugar without any disorders.
Broken Beta Cells
Beta cells do not always send the right amount of insulin. In case there is some disorder, cells may produce the wrong amount of insulin that influences the level of blood sugar. Take into account that the increased level of sugar may have a negative impact on the beta cells. The worst variant is when high blood sugar results in broken cells.
Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosis and Tests
Have you noticed any signs of type 2 diabetes? Then, don’t waste time and see your healthcare specialist who can determine the prediabetes stage. Only a competent doctor can make all the necessary laboratory tests and conclude whether you have type 2 diabetes or not. Type 2 diabetes signs aren’t enough for the diagnosis. Often, patients ask how many tests are needed to determine type 2 diabetes. If you have a high blood sugar level, it is enough to make one test to set a diabetes diagnosis (2d type). Those who have more than one sign of diabetes don’t need to spend days in the hospital to determine the presence of type 2 diabetes. But in most cases, tests are ready within a couple of days. What kind of testing can prove the type 2 diabetes diagnosis? Check them below.
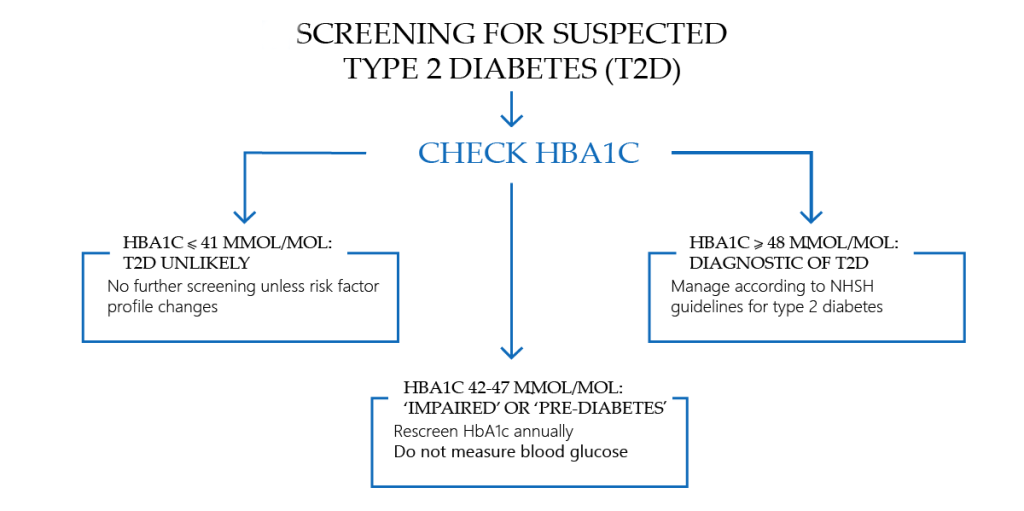
A1c
It is the test that is used to determine the level of glucose in your blood and all the changes that took place within 2-3 months. It’s a must test for the biological diagnosis of diabetes.
Fasting Plasma Glucose
It’s a must-have test to be diagnosed with diabetes. Remember that you mustn’t have food or drinks for 8 hours before this test. Otherwise, the result won’t be valid. The aim of the plasma glucose test is to identify the level of blood sugar you have at the moment.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
Compared to the previous test, here, you need to have a sweet drink before making an oral glucose tolerance test. Why do you need to make OGTT? It will show the reaction of your body to sugar. The tolerance test is one of the obligatory tests for everyone who has symptoms of type 2 diabetes. It’s very important to check whether you have high blood sugar or your body handles sugar without any disorders.
Type 2 Diabetes Treatments and Therapies
Unfortunately, it is hard to get rid of diabetes. Type 2 diabetes treatment consists of several constituents. You should follow all the doctor’s recommendations to live a normal life. It is up to you to develop healthy lifestyle habits and forget about the habits that could be harmful to your current condition. Take into account that there is no just one magic pill you could take and treat type 2 diabetes. What is type 2 diabetes? It’s the disease that will be with you for years. But don’t start panicking. It’s possible to live a decent life if you take medicines and change your lifestyle for the healthy one.
What exactly should you do to optimize the quality of life? In some cases, a healthy diet and special physical exercises can help achieve the normal blood sugar level even without taking any drugs. If you lose extra weight and eat healthy foods, you won’t suffer from any negative diabetes signs anymore. Diet does not mean fasting for weight loss, and exercise isn’t only about running on a treadmill to the point where the ground is slipping from under your feet. “Diabetes diet” refers to the type and amount of food. “Physical activity” means the need to play sports and lead an active lifestyle. Now that doesn’t sound so bad, does it? For both diabetics and healthy people, diet and exercise is the key to maintaining health and a balanced lifestyle.
Keep in mind that you need to consult with a dietician who will plan your daily ratio. Don’t do it on your own. You shouldn’t also decide on workouts without the doctor’s consultation as certain physical exercises may be harmful. There are several rules you need to follow to develop healthy eating habits.
Recommendations for healthy eating:
- Count the number of calories you consume daily, keeping in mind that your aim is to lose weight.
- Try not to eat candies and other products that contain refined carbs.
- Eat more veggies and fruits. It’s perfect when you include them in your ration regularly.
- Make sure that your body gets enough fiber.
Avoid eating foods listed below:
- starchy foods: bread, cereals, crackers, rice, pasta, cereals;
- starchy vegetables: potatoes, peas, beans, corn;
- fruit, fruit juices;
- milk, yogurt;
- sweets: honey, table sugar, syrup, jellies, candy, sports drinks, cookies, cakes, pastries, ice cream, puddings.
What kind of physical activity can be helpful? Doctors recommend doing physical exercises regularly. It is up to you to choose what kind of sports you like most. It can be a 30-min walk, biking, swimming, or any other physical activity you do during 30-60 min daily. Bear in mind that if you take drugs for lowering sugar in the blood, you should eat something before doing sports.
One more point to pay attention to is the necessity to check the blood sugar level on a regular basis. You should consult the doctor on the frequency of doing tests. This refers to all the patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, especially those who are insulin-dependent.
Have you been leading an active lifestyle but didn’t achieve the desired result (your blood sugar level is still where it was)? In such a case, you will be prescribed a medical treatment course. Many patients need to take drugs prescribed by the doctor to normalize the blood sugar level. The most common medications used for diabetes treatment are the following:
- Sulfonylureas.
- Metformin.
- Thiazolidinediones.
- DPP-4 inhibitors (e.g. Januvia).
- GLP-1 receptor agonists.
- Insulin.
Oral medicines can help people with type 2 diabetes control their blood sugar and work in one of five main ways:
- A decrease in insulin resistance. Metformin makes it so that the amount of glucose produced by liver cells drops. The drug reduces the rate at which glucose is absorbed from the intestines after meals.
- An increase in insulin secretion. Sulfonylurea and meglitinide preparations stimulate the secretion of insulin by the beta cells of the pancreas.
- A decrease in the absorption rate of sugar from the intestines. Acarbose is an enzyme targeting drug that actively targets alpha-glucosidase. This enzyme is critical for breaking down carbohydrates into sugars, which slows down the absorption of sugars after a meal and prevents spikes in blood sugar.
- An increase of the urinary glucose sediment. Gliflozin drugs are a relatively new form of drugs that start working after the kidneys have filtered out glucose. They inhibit the sodium-dependent glucose transporter, preventing the reabsorption of glucose into the bloodstream, allowing the body to excrete glucose in the urine, and lowering blood sugar levels.
- Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase. Glyptins, which are dipeptidyl peptidase inhibitors, prevent the breakdown of glucagon-like peptide-1, which, in turn, allows for higher postprandial insulin production.
Sometimes, one drug isn’t enough to control the blood sugar level. In such a case, the doctor will prescribe a combination therapy. Patients who have an increased blood sugar level, despite physical exercises, diet, and monotherapy (treatment with one medication), should take a combination of medications and measure the level of sugar regularly.
The main properties of antihyperglycemic drugs
| Risk of hypoglycemia/ weight gain |
Minimum*1 required GFR [mL/min] stated in physicians’ information, 9/2012 | Special properties | Typical application | |
| Metformin | no*2/no | 60 | gastrointestinal side effects are common, particularly at the beginning of treatment: start at a low dose! | first-line drug for type 2 diabetes |
| Sulfonylureas | yes/yes |
|
the sulfonylureas have been well established for many years as effective antihyperglycemic drugs | inexpensive combination partner for metformin; inexpensive alternative to metformin if the latter is contraindicated or poorly tolerated |
| Glinides | yes/yes | repaglinide*’: renal insufficiency is not a contraindication, dose adjustment recommended | more flexible than sulfonylureas because of their faster onset and shorter duration of action | superior to sulfonylureas if meals are taken irregularly or unreliably, as well as for patients with renal insufficiency |
| DPP-4 inhibitors |
no*2/no | sitagliptin, vildagliptin: 50, dose adjustment up to ESRF saxagliptin: 60. with dose adjustment as low as 15, not recommended in ESRF linagliptin*6: no dose adjustment required, even in severe renal insufficiency | advantage compared to GLP-1 receptor agonists: oral administration | inadequate glycemic control with metformin alone, elevated risk of hypoglycemia, overweight |
| SGLT-2 inhibitors |
no*2/no | 60 (dapagliflozine) | weight loss; elevated risk of genital infections | inadequate glycemic control with metformin alone, elevated risk of hypoglycemia, overweight |
| GLP-1 receptor agonists |
no*2/no |
|
given subcutaneously; more effective than the DPP4 inhibitors, with the added advantage of weight loss | inadequate glycemic control with metformin alone, elevated risk of hypoglycemia, overweight |
| Acarbose | no*2/no | 25 | gastrointestinal side effects are common (flatulence) | early type 2 diabetes, or else as combination partner |
| Pioglitazone*3 | no*2/yes’4 | 4 | risk of fluid retention and cardiac insufficiency; increased propensity to bone fractures; possibly increased risk of bladder cancer | combination partner for patients at elevated risk of hypoglycemia and those with severe renal insufficiency |
| Insulin | yes/yes | no restriction | necessary in advanced stages of the disease; may be reasonably combined with metformin |
GFR, glomerular filtration rate; DPP-4, dipeptidyipeptidase-4; GLP-1. glucagon-like-peptide 1 ESRF: end-stage renal failure.
M Patients with inadequate metabolic control under oral antidiabetic treatment, a tendency to hypoglycemic episodes, or worsening of their general condition should be treated with some type of insulin therapy regardless of whether their renal clearance is normal or impaired. This holds especially for patients with highly variable renal function (www.diabetes.versorgungsleitlimen.de (27]).
Statement not valid when this drug is used in combination with a drug that can cause hypoglycemia.
‘3 Pioglitazone was removed from the list of reimbursable drugs in the German statutory health insurance system in March 2011.
Weight gain affects primarily subcutaneous fat rather than the metabolically more harmful visceral fat 5 Exenabde: not applicable for the long-acting formulation of the drug.
‘* Not available in Germany.
‘T Nateglinide is approved only for use in combination with metformin and therefore cannot be given to patients with renal insufficiency.
How to Prevent This Type of Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes mellitus occurs in 10-15 % of all diabetes mellitus cases. The remaining 85 – 90 % account for type 2 diabetes mellitus or non-insulin-dependent diabetes. As the name suggests, the lack of insulin has little to do with it. In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas initially works as it should. If you have this disease, your muscle tissue, for which glucose is the main energy supplier, is unable to use the insulin produced by the body. Its cells practically cease to receive vital glucose. This condition is called insulin resistance (tissue insensitivity to insulin). Insulin resistance can be an inherited congenital defect but is most common in people suffering from excess weight. According to statistics, more than 80% of patients with diabetes mellitus are overweight.
This means that if you want to prevent type 2 diabetes, you should eat healthy foods, avoid stress, and do physical exercises regularly.
Recommendations for lifestyle changes to prevent type 2 diabetes:
- Reduce the number of foods high in fat and digestible carbohydrates in your diet. You should use mainly lean meats, fish, preferably boiled, baked, and stewed, but not fried.
- Increase the proportion of low-calorie foods and foods rich in plant fiber (various types of cabbage, carrots, radishes, green beans, rutabagas, bell peppers, eggplants, etc., unsweetened fruits).
- Adhere to the “food pyramid” principle, which helps you easily form a healthy diet and get all the nutrients you need in optimal amounts.
- Get at least 2.5 hours per week of moderate physical activity, such as walking at a brisk pace. Increasing physical activity to intense activity is twice as beneficial and can provide additional health benefits.
- Do not deviate from these recommendations as these simple lifestyle changes will allow you to prevent not only the development of type 2 diabetes but also other serious diseases associated with diabetes – stroke, heart attack, gangrene of the extremities.
Risks and Warnings
Type 2 diabetes is a serious disease that can prevent you from living a full-fledged life if you don’t follow the doctor’s recommendations. Patients with an abnormal level of blood sugar suffer from heart diseases, have problems with kidneys, and often need dialysis. Diabetes has a negative impact on the nervous system, sexual sphere, problems with vision (even blindness sometimes). If a woman has been diagnosed with diabetes, she should do her best not to get pregnant as there is a high risk of miscarriage. Keep in mind that the baby may have unwanted defects because of diabetes. One more thing to keep in mind is that depression and diabetes are interconnected.
As you can see, people with type 2 diabetes suffer from different health problems that aren’t always compatible with a happy life. That’s why you should do your best to prevent the development of this disease by following the recommendations listed above.


























