Medications for Type 2 Diabetes
If you faced the diagnosis of type 2 diabetes, you are not alone in this. It is remarkable that, unfortunately, more children and teenagers are being affected by the condition. Diabetes is a complex medical disorder made up of several factors forming the disease's overall picture. It is the condition when the body is not able to make sufficient amounts of the hormone insulin to control blood sugar levels. Its treatment is never easy and, what is more, requires a smart approach. That's why your doctor will consider a wide range of variables before recommending any form of medicine for managing type 2 diabetes mellitus.
These factors might most surely include:
- Possible side effects of the therapy.
- Effectiveness of treatment if there are other chronic diseases in the background (such as heart failure, liver or kidney illnesses, being overweight).
- The condition of a patient's heart.
- Average blood sugar levels for a patient, usually based on an A1C test.
- Body weight and the relation of a drug's activity to the changes in body weight.
- A medication's affordability.
The results of an A1C test (measuring the average blood glucose) will also tell the doctor if it will be enough to use one medication for a patient or two of them simultaneously. The process of treatment also requires careful supervision. Only your doctormay prescribe a treatment plan in order to prevent common issues without harming the patient's health, and prescribe the proper types of drugs for type 2 diabetes.
Best Medications for Type 2 Diabetes
People who intend to begin their diabetes treatment have an overwhelming amount of alternatives available to them in the world of medicine. All those treatments, however, differ from one another, and the best results only come through pre-screening with medical research. Contrary to popular belief, not all patients will benefit from a treatment like insulin injections.
The severity of insulin insufficiency is classified by doctors. Non-insulin medications work better when blood sugar levels are closer to normal.
The following drugs stand out as the top treatments for type 2 diabetes, according to specialists (see the list of medications to treat type 2 diabetes).
Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors
This type of medication for type 2 diabetes is prescribed to individuals to help them handle starchy food, which is supposed to lower one's blood sugar. Acarbose slows down the body's absorption of carbs and aids in the digestion of simple sugars. Doctors usually prescribe to use them before the meal. In any case, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors are rarely used by doctors. There are undoubtedly other excellent treatments for type 2 diabetes.
Biguanides
This medication works in a completely different direction.
To regulate the levels of glucose that the liver produces, biguanides are used. Its main advantages include improving your body's sensitivity to insulin and assisting your muscles' cells in properly absorbing and using this glucose.
The most well-known member of the biguanides family is probably metformin, which works well in combination with other drugs.
Dopamine Agonist
One of the oral treatments for type 2 diabetes, Cycloset is also known as Bromocriptine, has not yet had its mechanisms of action well explored. It's known that it changes the way the human brain perceives dopamine by increasing the sensitivity of dopamine receptors together with making the body more sensitive to insulin. Its advantage is that during the medication's intake, the body doesn't need as much insulin to make use of glucose as it used to.
However, it's wrong to consider these tablets a panacea - the drug works well only if integrated with a healthy lifestyle.
Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors
According to the study, this is a safe medication affecting several body mechanisms at once - stimulating insulin secretion, slowing down the gastric response to the taken nutrients, and regulates glucose through the interaction with the enzyme DPP-4, which is responsible for the expression of the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide. Patients who received therapy with sulfonylureas and metformin but saw little to no change throughout treatment are highly appreciative of its originality and primary usage.
Dipeptidyl peptidase inhibitors include a set of medications such as Linagliptin, Galvus, and Januvia.
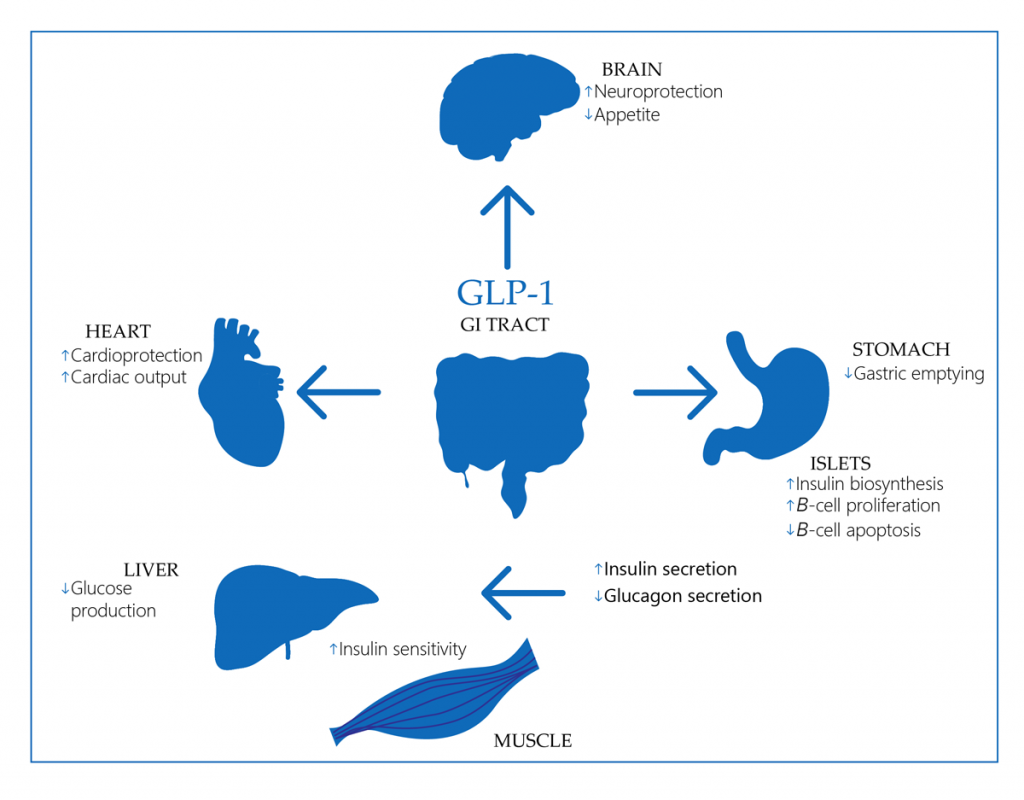
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists
The drug is a widespread one among the new medications for diabetes type 2 and shows effectiveness in affecting the incretin system. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist balances the hormonal response to nutrients and lowering blood sugar back to normal. The image below illustrates how it would behave logically.
Meglitinides and Other
Repaglinide and nateglinide are the most often prescribed meglitinides to patients whose beta cells are dysfunctional. FDA-approved for type 2 diabetes, the medication is typically used in conjunction with other treatments.
Other most common medications for treating type 2 diabetes include:
| Sulfonylureas | A suitable version for a tight budget that makes the pancreas produce insulin |
| Thiazolidinediones | This medicine gives the pleasant bonus - increasing good cholesterol in the blood |
| Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors | Prompt a gradual weight loss thereby lowers blood pressure |
| Bile acid sequestrants | Works well in cases with serious liver problems |
Other Useful Medications for Type 2 Diabetes
Apart from the main medicines helping patients to lower blood sugar and improve glucose absorption by the cells, there might be other most common medications for coping with type 2 diabetes - those that lower cholesterol, normalize blood pressure, or prevent cardiovascular diseases.
Aspirin for Heart Health
Research published by American Diabetes Association back in 2004 has revealed a number of benefits that aspirin can give to people who are at high risk of atherosclerosis and vascular thrombosis. Its usefulness was proven in the experiment with people rehabilitating after myocardial infarction and cardiovascular surgeries along with patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The latter group showed a 44% heart disease risk reduction.
Drugs for High Cholesterol
Statins, or medicines used for controlling cholesterol, have proven efficacy also for curing type 2 diabetes. Very high cholesterol levels are directly associated to insulin resistance, a hallmark of prediabetes, therefore the two medical disorders coexist. What happens when a patient with both conditions starts to take statins such as Fluvastatin, Lovastatin, or Simvastatin? The anti-inflammatory effects and the prevention of fat buildup in the arteries are amazing at lowering the damage brought to arteries by atherosclerosis by more than a half.
High Blood Pressure Medications
This group of medications is directed for the use of patients who have the symptoms of hypertension along with type 2 diabetes. As statistical data reveals, patients with type 1 or 2 diabetes have 2 times more chances to suffer from hypertension - chronically high blood pressure. This condition, in turn, can lead to a heart stroke. In such cases, doctors recommend sticking to a healthy diet (DASH diet), watching your weight, and taking tablets such as ACE inhibitors, ARBs, and diuretics.
Both ACE inhibitors (such as lisinopril) and ARBs (such as losartan) have a tendency to activate the kidneys, causing the fluid to exit the body more quickly and lowering blood pressure as a result. In order to ensure that your kidneys are healthy before taking them, you must perform several tests. Diuretics, sometimes referred to as "water tablets," operate almost identically but have an impact on your electrolyte balance.
Popular Supplements for This Type
In the war against type 2 diabetes, one can greatly improve their condition by additionally taking herbs or vitamin supplements to meet all the body's needs. Sometimes people want to use these supplements to replace drugs, while on other occasions they work great as additions to the primary prescription.
Chromium
This supplement is intended to restore the metabolism of carbohydrates to normal. If used in small doses, the supplement is safe for the majority of individuals with conditions. In any case, you should talk to your doctor about this because increasing the dosage might eventually lead to dangerously low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia).
Magnesium
The spectrum of this chemical is really wide - from keeping our nervous system healthy to eliminating oxidative stress. Magnesium is usually taken in the form of supplements when there is not enough magnesium in the diet (still, it's always better to take it with food). Its effectiveness is widely researched - magnesium improves sensitivity to insulin and regulates blood pressure in diabetics.
Cinnamon
It is amazing what benefits different spices and herbs have on the body. It's as though nature is trying to cure us. Every individual with type 2 diabetes has to include cinnamon in their diet since it is such a potent addition. Its main plus is lowering fasting blood glucose levels, as proven by 2011 research.
Other beneficial add-ons include alpha-lipoic acid that shows brilliant results in increased sensitivity to insulin, green tea that is rich in antioxidants that prompt insulin activity, resveratrol that prevents blood sugar from rising too high. The latter is present in many grape varieties including red wine, but you should still talk to your doctor before drinking any alcohol.
How to Choose The Right Medicine
Now that there are many drug alternatives available to manage diabetes, it is critical to select treatment options based on your unique requirements and preferences. Modern medicine tends to avoid insulin injections when it is possible. The majority of patients begin with what is known as non-pharmacological therapy, which entails regular exercise and diet correction so that they may obtain the necessary vitamins and minerals from nutritious food. Physical activity is also a must for everybody struggling with the choice of treatment since none of the medical supplements will be effective without an appropriate lifestyle. The greatest thing you can do initially is to introduce lifestyle adjustments if the choice of drugs is largely up to the doctor.
Age is another important consideration when choosing a medicine because treatments vary depending on the age of the patient.
For Adults
Adults treated with metformin, sulfonylureas, swift-acting meglitinides, and the class of drugs that increase insulin sensitivity typically exhibit considerable improvement - thiazolidinediones, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, etc.
Early pharmacologic therapy in adult patients has promise for improving glycemic control and reducing complications in the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Other important pieces of advice that go along with medical supplements include:
- Having meals scheduled.
- Eating only till you are full (no overeating).
- Increasing the amount of fiber that is contained in fruit, vegetables, nuts such as almonds and pecans.
- Replacing fast carbohydrates with slow ones (whole grains, e.g. quinoa and oats).
- Cutting down on processed food and those containing too much salt.
- Topping up the omega-3 intake, which is vital for heart health.
For Children and Teens
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes in children are more challenging to notice. The same chronic fatigue, the lack of energy, excessive urination, unusual thirst, and cuts that heal slowly are some of the first signs that a child's blood sugar is above the norm. However, each kid shows them individually, let alone the fact that many children don't show symptoms at all. And there is another good reason to have frequent medical checkups. To reduce the likelihood that a child may develop type 2 diabetes, parents should keep an eye out for the symptoms described, monitor their child's blood glucose levels, and adopt good lifestyle practices.
Depending on the stage of type 2 diabetes, children might be treated with the same drugs as adults, except for a different dosage. Young individuals respond well to meglitinides, sulphonylureas, glitazones, biguanides, and several analogs of amylin.
Oral Medications for Type 2 Diabetes
In a nutshell, anyone choosing a medicine to treat type 2 diabetes is faced with a decision between diabetic pills and insulin injections. The history of the disease (how long you've had it) and the levels of insulin your body is meant to naturally produce in a healthy condition are taken into consideration by doctors when prescribing dosage instructions.
Although using oral drugs is undoubtedly more convenient, whether or not you also need to add insulin injections depends on the specifics of your treatment plan. Insulin, in case of overdose, has heavy complications, so never try to experiment with the dosage defined by the doctor.
Fortunately, a wide variety of oral drugs are effective enough to keep diabetes under control and allow patients to enjoy remission. The drugs that are compared to insulin based on their activity include Acarbose, Nesina, Bromocriptine, Canagliflozin, Diabinese, Cycloset, Glyset, and many others. Your doctor might assign one of them either as a key element in treatment or as an additional supplement.
How Does Insulin Therapy Work
Insulin injections are used to control blood glucose both in cases with type 1 and type 2 diabetes when the patient's condition cannot be kept stable just by oral medications. Basically, injected insulin takes the place of the natural insulin aiding the body to use the sugar from the blood for healthy cell functioning. It provides the cells with energy and improves their cellular metabolism.
Insulin is injected a few times a day, so there are actually several types of it needed for a patient. The first several times when insulin is injected into a vein, a nurse or doctor has to observe a patient's reaction for any side effects.
Do not change the type of insulin without receiving a direct recommendation from your doctor. It is also advised to check if your insulin is transparent, colorless, and homogeneous. If you have an allergy to any form of insulin, let your doctor know before beginning insulin therapy. Mention also any supplements, herbs, or non-prescribed medicines you are taking and discuss how you will use them when traveling, change exercise activity, or experience stress.
This infographic explains insulin treatment the best.
When to Contact a Doctor
Contact your doctor as soon as you have any adverse effects to discuss how to increase your medication dosage this week, when to give yourself an insulin shot, how to inject the medication correctly, how to store it, and other issues. When you intend to switch the type of insulin you are taking, you should definitely call your doctor. Since each of them has its instructions that have to be strictly followed, make sure you talk it over with the doctor.